Table of Contents
Introduction to Oracle Virtual Box
Oracle Virtual Box is a product of Oracle, it is one of the most popular and powerful open-source tools that helps to create a Virtual Machine in a few minutes without hampering the actual physical machine.
Users can run different operating systems on a single physical machine by using Oracle Virtual Box, a free and open-source virtualization application. Its extensive feature set, versatility, and ease of use are well known.
On a single physical machine, users can create various operating systems such as Windows, Linux, or macOS by creating and running virtual machines (VMs) on their computer.
Why Use Virtualization?
Virtualization is a common practice in modern computing because of its various features which are as below: –
1. Cost Efficiency: Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, reducing the need for more hardware.
2. Better Resource Utilization: With virtualization, resources like CPU, memory, and storage can be allocated more efficiently. Instead of having servers underutilized, multiple VMs share resources dynamically, maximizing the hardware's potential.
3. Flexibility and Scalability: Virtualized environments are highly flexible. New virtual machines can be created, deployed, or removed quickly, making it easier to scale operations up or down based on demand.
4. Isolation and Security: Each virtual machine operates in its environment, isolated from others.
5. Simplified Management and Maintenance: Virtual environments allow for easier management through centralized control panels. Several VMs can be managed, troubleshooted, and monitored by administrators from a single location, which streamlines processes. Moreover, it makes migration, recovery, and backup operations easier.
6. Testing and Development: Virtualization makes it easy to create test environments that replicate real-world scenarios without the need for dedicated physical servers. Developers can experiment and test new software or system configurations without risking the main system.
7. Disaster Recovery: Virtualization enhances disaster recovery by making it simpler to back up and restore entire virtual machines. In case of a hardware failure, a VM can be moved to another server or restored from backup, ensuring business continuity.
In summary, virtualization plays an important role in today's IT environment because we can create n number of machines for practice, testing, and other major application releases and destroy them when all the testing is complete in minutes without impacting the actual physical machine.
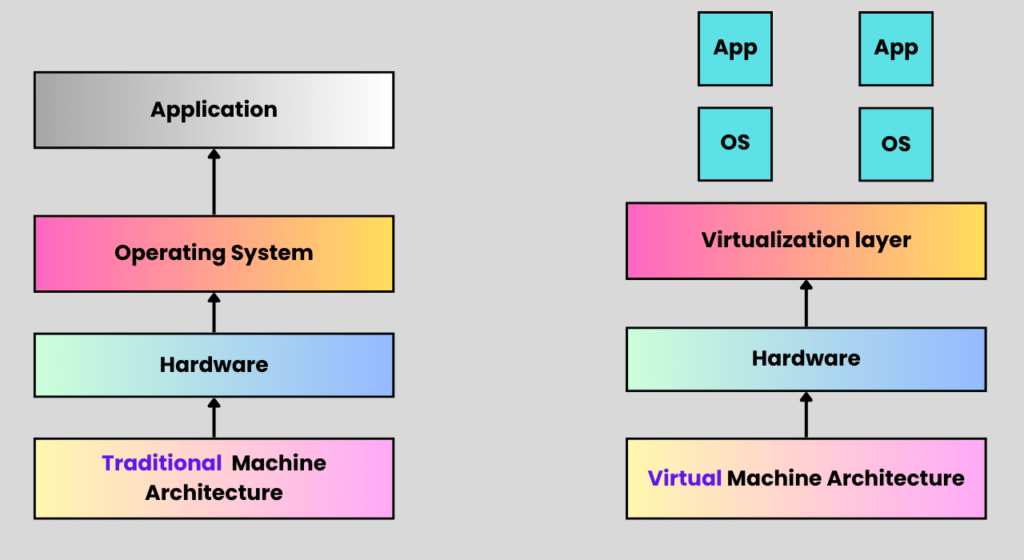
Traditional Machine Architecture vs Virtual Machine Architecture
There are 2 different types of methods are there to create a machine that uses computing resources. The first one is a Traditional machine and the second one is a Virtual machine.
Traditional Machine Architecture
In traditional machine architecture, a physical server runs a single operating system directly on the hardware. Here’s how it typically works:
1 . Single Operating System: Each physical machine operates with one installed operating system (OS). This OS has full control over the hardware resources—such as CPU, memory, and storage—and manages the applications running on the machine.
2. Dedicated Hardware: The operating system and applications run directly on the machine's hardware. This means that each machine is dedicated to a single task or set of tasks, which can lead to underutilization if the workload does not fully consume the system's resources.
3. Scalability Limitations: If an organization needs to add more services or computing power, it often requires purchasing additional physical servers, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4. Failure Impact: If the hardware or operating system fails, all services and applications running on that server stop functioning, leading to potential downtime. Recovery or repair can be slow because it requires troubleshooting the physical machine.
5. Resource Wastage: Often, a single server’s full capacity is not utilized. If a server is only running one application, but has significant unused CPU or memory, that excess capacity goes to waste because it cannot be allocated to other workloads.
Virtual Machine Architecture
Virtual machine (VM) architecture, on the other hand, uses a layer of software called a hypervisor to allow multiple virtual machines to run on the same physical hardware. Each virtual machine functions as if its own computer, complete with its own operating system and applications. Here’s how it works:
1. Multiple Operating Systems: A single physical server can host multiple virtual machines, each with its own operating system (which can be different from one another). This allows for greater flexibility since you can run Linux and Windows on the same physical machine.
2. Hypervisor Layer: The hypervisor is a key component that sits between the physical hardware and the virtual machines which helps to manage the distribution of physical resources—such as CPU, memory, storage, etc.
3. Better Resource Utilization: Since multiple VMs share the same physical hardware, resources can be dynamically allocated based on the needs of each VM.
4. Easy Scalability: Virtual machine architecture is highly scalable. Adding a new VM or reallocating resources to an existing one is fast and doesn’t require purchasing additional physical servers.
5. Improved Fault Tolerance: Since virtual machines are independent of one another, a failure in one VM won’t affect the others. Additionally, if the underlying hardware fails, VMs can be migrated or restored to a different server relatively quickly, reducing downtime.
6. Isolation and Security: Each VM is isolated from others, so applications running on one VM won’t interfere with those on another.
Installing Oracle Virtual Box
System Requirements
We need to ensure that our system is meeting the requirements before proceeding further.
1. At least 4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended)
2. 20 GB of free disk space
3. A modern processor with hardware virtualization support (Intel VT-x or AMD-V)
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for Oracle Virtual Box
1. Please go to the Oracle Virtual Box website and click on the “Windows host” option to download it.
2. On your PC, the Virtual Box executable file will begin to download.
3. Run the file and set it up where you want it.
Creating a New Virtual Machine (VM)
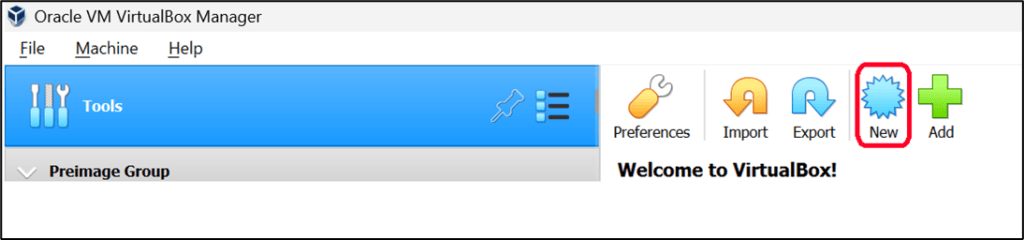
1. You need to click on “New” in the virtual box interface to create the virtual machine.
2. A new prompt will come when you need to give a Name and select the OS as per your requirement.
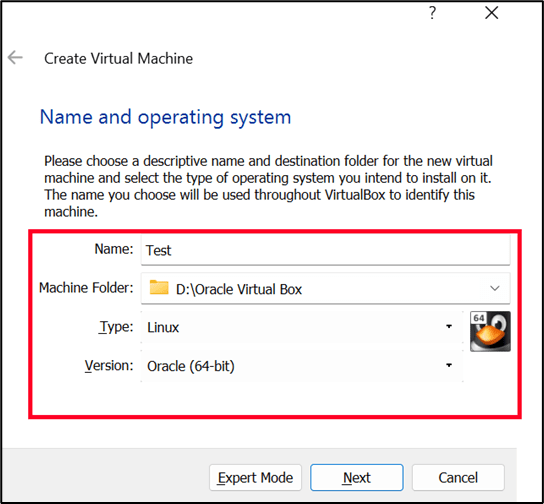
3. Now you need to give the allocate below details as per your hardware capacity and then at last click on “Create”

4. Now before installing the operating system, we need to do some of the General settings which are as follows.

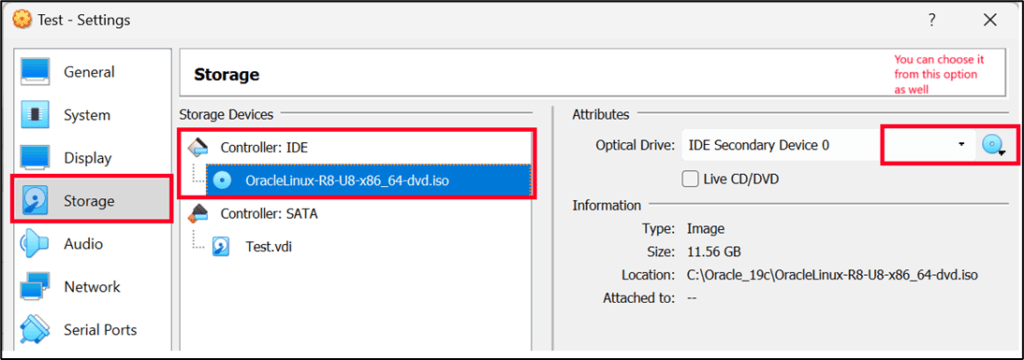
Installing an Operating System on a VM
After doing all the basic settings now we can proceed further with Installing an Operating System on a VM. You need to follow the below steps to do the same.
1. Click on the Start tab.
2. Choose this option Install Oracle Linux on 8.8.0 and press Enter.
Note: – You can choose the ISO image as per your requirement.
3. Choose the Language as English (United States).
4. We need to complete this step one by one like Installation Destination==> Software Selection==> Network & Host Name==> Time & Date ==> Root Password and then click on Begin Installation
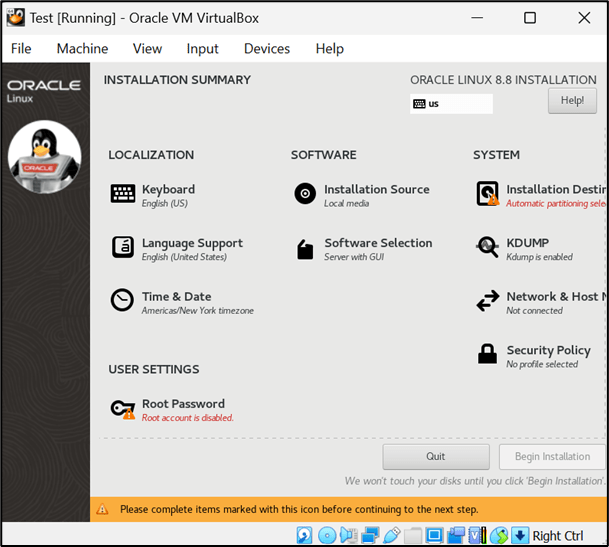
Note: – Please check the below details if you have any kind of confusion regarding the Installation Summary. I have explained the above steps through the below points to clear out the confusion.
a. Installation Destination==>Select Local Disk==>Custom==>Done
Partition Details: –
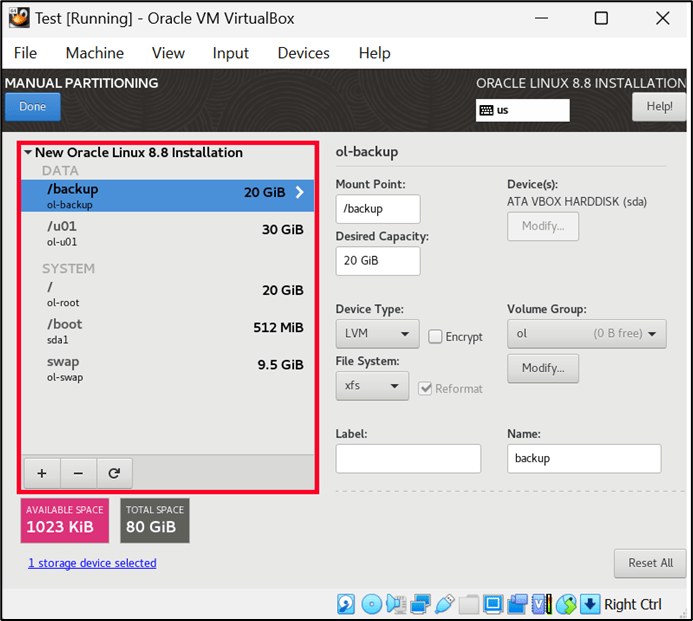
b. Software Selection==> Server with GUI
c. Network & Host Name==> Host Name (as per your requirement)
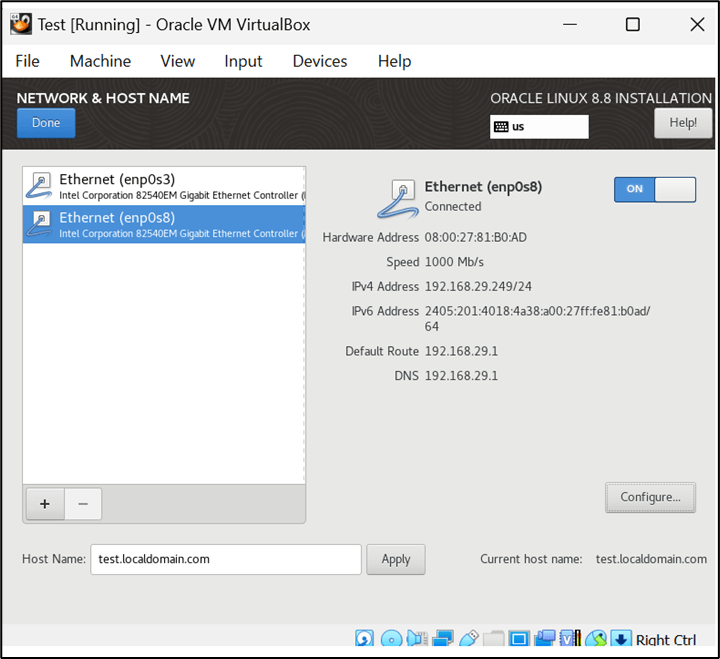
Network & Host Name==> enp0s3—Configure—(General—Click automatically with Priority—Ipv4 settings (Give IP address as per your requirement)—Ipv6 setting—choose Ignore) – OFF and ON Setting)
Network & Host Name==>enp0s8—Configure—(General—Click automatically with Priority—Ipv4 settings (Choose Automatic DHCP—Ipv6 setting – choose Ignore) – OFF and ON Setting)
d. Time & Date==> You can set it as per your time zone.
e. Root Password==> You can set it as per your standard.
Setting of Network & Host Name: –
5. Installation is in Progress of Oracle Virtual Box
6. Reboot the system once the installation setup is completed.
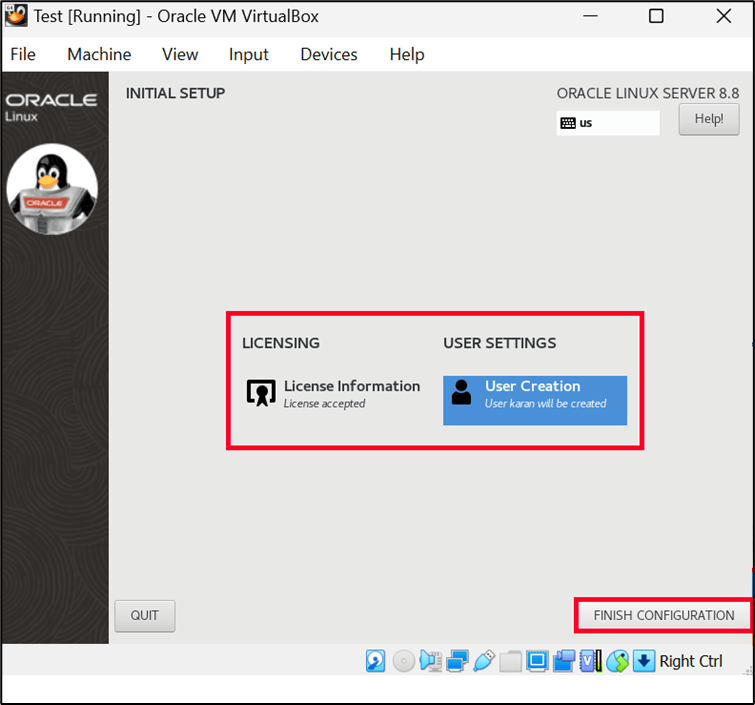
7. Now accept the License agreement as well as create a user and then click on Finish Configuration.
As we can see below output Screen resolution is not as appropriate as we want because it is not opening in full screen also sharing the folder will not work yet, To resolve these issues we need to install Guest additions for our Oracle Virtual Box which we will see in the next blog.
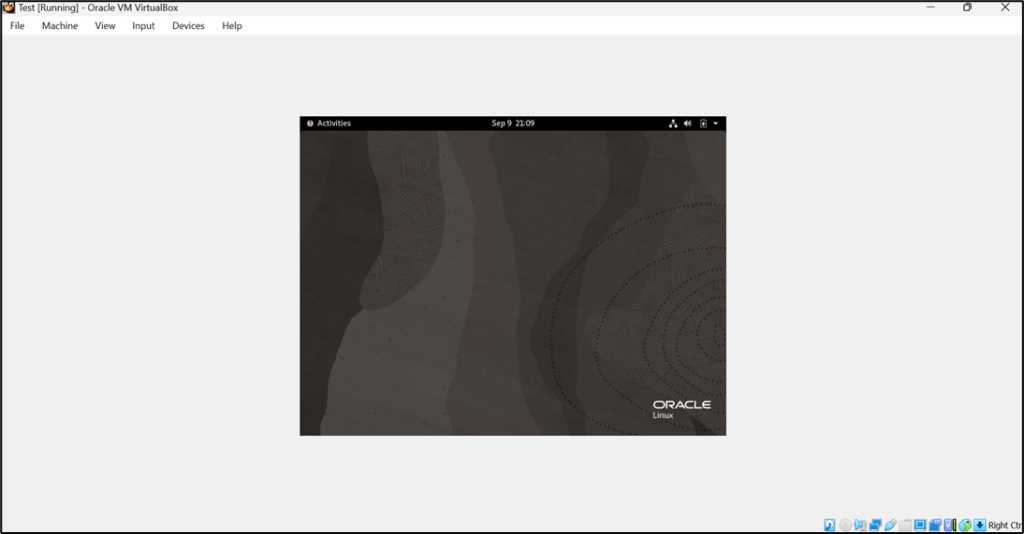
Finally!! We have Installed the Oracle Virtual Box.
Conclusion
We can build n virtual computers on a single physical machine by using Oracle Virtual Box.
FAQ's
Is Oracle VirtualBox free to use?
Yes, VirtualBox is open-source and free for personal and commercial use.
Can VirtualBox run macOS on Windows?
Technically yes, but running macOS on non-Apple hardware (Hackintosh) is against Apple’s licensing agreement.
How to increase performance in VirtualBox?
You just need to provide enough CPU and memory to the virtual machine and you will see your machine will work perfectly with any hanging issues. You can also install the guest additions of Virtual Box and a few more VM settings.
How do I install VirtualBox guest additions?
When you install the Guest additions then you will see the improvement in Virtual machine performance as well the user experience, Display resolution, and folder sharing options are also enabled. You can check out this article to learn how to install Virtual Box guest additions.
Can I run multiple VMs simultaneously in VirtualBox?
Yes, but you need to keep a few things in your mind, especially the hardware, if you have specifications then you can run multiple VMs at the same time.